 |
|
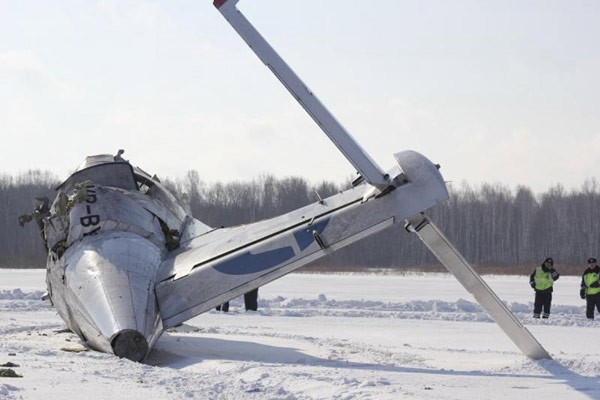
Emergency service workers stand near the tail section of the UTair airlines ATR 72 passenger plane that crashed near the Siberian city of Tyumen April 2, 2012. [Photo/Agencies]
|
 |
|
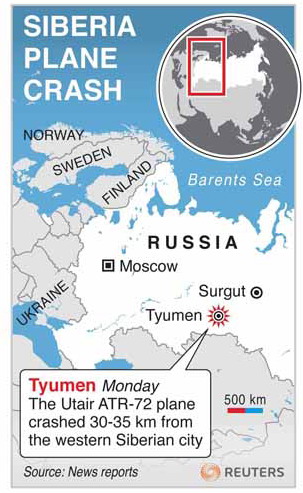
Map locating Tyume, Siberia, where a passenger plane with 43 people on board crashed on Monday. [Photo/Agencies] |
Thirteen survivors were pulled from the wreckage and rushed to hospital by helicopter but one later died. Television footage showed the plane, which had broken in two, lying in a snowy field. Only the tail and rear part of the fuselage were visible.
It was not immediately clear what caused the UTair airlines ATR 72 to crash with 39 passengers and four crew on board, the latest air disaster to blight Russia's safety record.
"There are no explanations yet," Yuri Alekhin, head of the regional branch of the Emergencies Ministry, told Russian television from the scene of the crash.
He said the "black box" flight recorder had been found and added: "Contact was lost with the plane just over three minutes after take-off."
UTair said on its website that the twin-engine, turbo-prop plane had been trying to make an emergency landing when it came down 1.5 km (one mile) from the airport in the western Siberian city of Tyumen en route to Surgut, an oil town to the northeast.
At least five of the survivors were in critical condition, RIA news agency quoted hospital officials as saying in Tyumen, some 1,720 km (1,070 miles) east of Moscow.??
| ?
 |
|
Emergency service workers investigate the wreckage of the UTair airlines ATR 72 passenger plane that crashed near the Siberian city of Tyumen April 2, 2012. [Photo/Agencies]
|
Russia's poor safety record
UTair has three ATR-72 craft made by the French-Italian manufacturer ATR, according to the Russian airline's website www.utair.ru.
ATR is an equal partnership between two major European aeronautics players, Alenia Aermacchi, a Finmeccanica ?company, and EADS. ? ? ?
The crash was the deadliest air disaster in Russia since a Yak-42 plane slammed into a riverbank near the city of Yaroslavl after takeoff on Sept. 7, 2011, killing 44 people and wiping out the Lokomotiv Yaroslavl ice hockey team.
President Dmitry Medvedev called for a reduction in the number of Russian airlines and improvements in crew training after that crash, which followed a June crash that killed 47 people including a navigator who had been drinking.
The International Air Transport Association said in December that global airline safety rates had improved in 2011 but that in Russia and the Commonwealth of Independent States, which groups former Soviet republics, the rate had risen.
Gunther Matschnigg, IATA senior vice-president for safety, said a key problem in Russia was that pilots and ground technicians were having to adapt to a growing number of a highly sophisticated aircraft.
He said Russian aviation officials and political leaders had accepted that pilot training needed rapid improvement.??