Brussels should 'de-ideologize' its approach
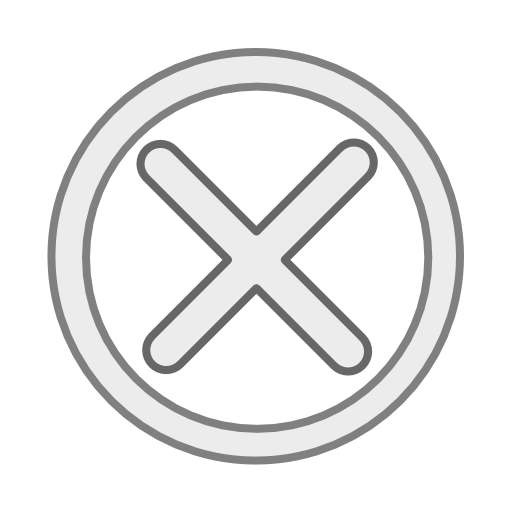
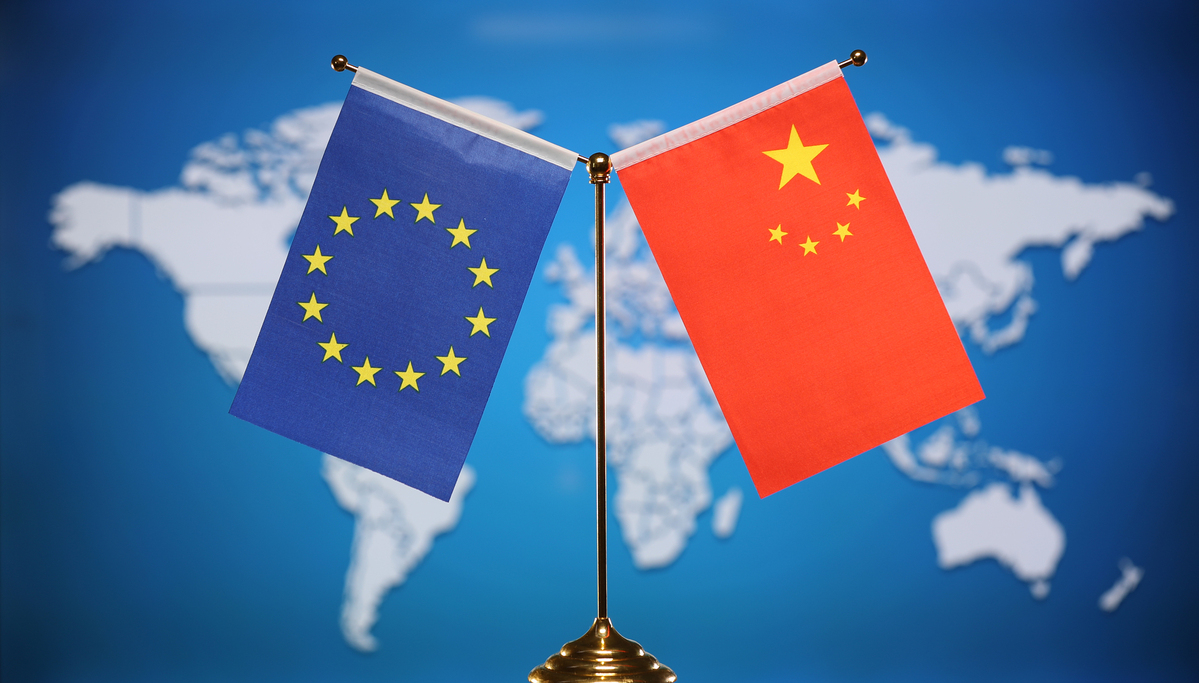


As the recent 24th China-EU Summit seems to have made headway in helping bring the two sides' comprehensive strategic partnership back on track, I am cautiously upbeat about the development of one of the world's most important political and economic relationships in 2024.
However, I am also more convinced than ever before that the European Union needs to "de-ideologize" its relationship with Beijing by, for instance, throwing its emphasis on "de-risking" and "systemic rivalry" rhetoric overboard, and returning to pragmatic realism, that is, dealing with China-EU matters in a sensible, practical and mutually beneficial manner.
Brussels should accept the fait accompli that China's political system is different to the one in the EU and that it would be foolhardy trying to foist the West's "values" on China, the world's oldest extant body politic.
What matters most is that the relationship between the two economic and trade giants benefits their 1.86 billion people, or 22 percent of the world's population. Besides, pragmatic China-EU ties are also advantageous to our troubled planet's development as a whole.
I hope European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen and European Council President Charles Michel will periodically subject themselves to a reality check as far as China-EU relations are concerned.
Von der Leyen's term expires next year, but she still hasn't revealed whether she will put herself forward for a second five-year term after the European Parliament election next June or, as some analysts say, is angling for the post of NATO secretary-general instead. Michel's second and final two-and-a-half-year term ends in November 2024. It remains to be seen what the possible (Von der Leyen) and certain (Michel) exit from the top of the EU will mean for the future of China-EU ties.
Brussels says the EU's trade deficit with China amounts to about $430 billion. While some 9 percent of EU exports last year were shipped to China, the latter accounted for about 21 percent of its imports. In 2022, China was the EU's third-largest export market (after the United States and the United Kingdom) and its top source of imports.
Mutually beneficial political, commercial and economic relations between Brussels and Beijing are, no doubt, advantageous to China's two special administrative regions, Hong Kong and Macao.
The EU is Macao's second-biggest source of imports, after the Chinese mainland. As such, Macao is doing its part, based on the comparatively small size of its import-export sector, to help the EU ship its products overseas.
Having formal links with the EU, Macao signed a trade and cooperation agreement in 1992 with the then European Economic Community, which was succeeded by the EU a year later. Irrespective of the name change, the deal remains in force. Based on the agreement, Macao also maintains an economic and trade office in Brussels. Hong Kong, however, doesn't have a similar pact with Brussels.
Also, the Institute of European Studies of Macao is holding master's degree courses in cooperation with the University of Macau. Since its launch nearly three decades ago, it has fostered closer ties between Macao and the EU, and strengthened local students' knowledge of European affairs and languages.
I expect Macao to remain committed to performing its historic role as a centuries-old hub of commercial and cultural exchanges between China and Europe — free of ideological constraints.
The views don't necessarily reflect those of China Daily.
The author is the director of the Macau Post Daily.
If you have a specific expertise, or would like to share your thought about our stories, then send us your writings at opinion@chinadaily.com.cn, and comment@chinadaily.com.cn.