Novozymes bets on China's green push


Danish biotech firm sees potential in nation's efforts toward carbon goals
Danish biological products provider Novozymes is eager to capture opportunities in China by intensifying its focus on innovation and offering localized biotech solutions, the company said.
China's optimized COVID-19 response measures have supported the development of the private sector, and helped attract more foreign investment, Novozymes said.
Despite headwinds from the pandemic, Novozymes' China business has played an important role in its overall strategy. In 2022, the company's sales grew 9 percent in both emerging and developed markets.
The nation is striving to peak carbon emissions before 2030 and reach carbon neutrality by 2060.
The company said it is pleased to see the Chinese government's efforts to optimize the investment environment for foreign investors and encourage innovation in new energy, green and low-carbon technology as well as demonstration pilots.
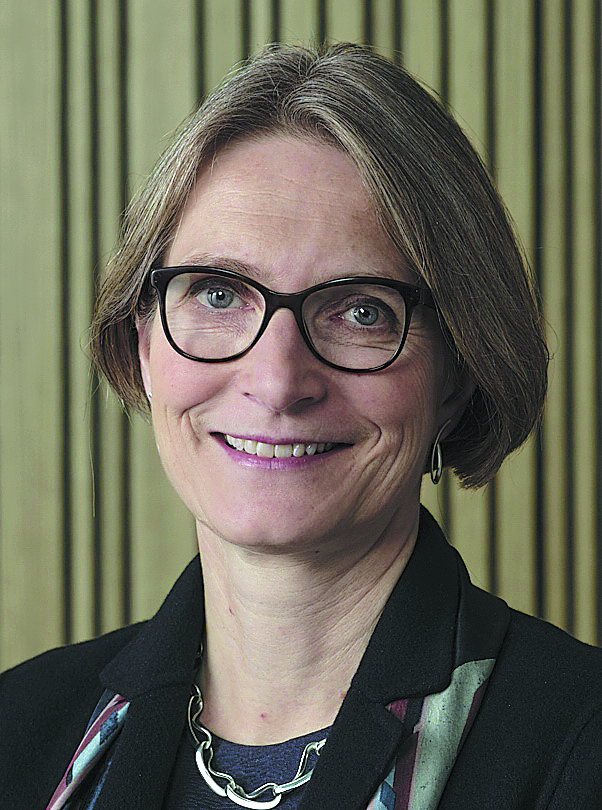

"China's pledge to achieve carbon neutrality and the comprehensive policy framework put in place to reach this goal will bring more opportunities. It will stimulate green transformation opportunities in various sectors, creating a demand for sustainable solutions," said Tina Sejersgard Fano, executive vice-president of Novozymes.
"As a biotech powerhouse, Novozymes will continue to leverage our expertise in low-carbon technologies to help more Chinese customers achieve their sustainability objectives," said Fano, who was in the country recently to attend the 15th China Bioindustry Convention in Wuhan, Hubei province.
Over the past few decades, Novozymes has invested in local manufacturing, research and development capabilities, as well as domestic talent.
The effort has enabled Novozymes China to become an important growth engine and a key R&D and manufacturing hub for the Danish company.
Biotech will play a critical role in reusing organic waste through waste-to-energy applications, including agricultural waste (biomass), waste oil and fats.
China's annual output of various types of such non-grain biomass resources exceeds 3.5 billion metric tons, including 960 million tons of agricultural waste and 350 million tons of forestry waste, according to Sequoia Capital.
Enzymes are proteins that can be used in biological feed, which is safe, environmentally friendly and residue-free, an industry report on China's biological feed industry showed.
Compared to conventional carbon capture, enzymatic carbon capture has the potential to become a stable and cost-effective solution for capturing carbon dioxide.
Carbon capture with enzymes could allow the use of waste heat, reduce capital expenditure and lower temperatures, which will bring more sustainable profits to businesses, Novozymes said.
"Biotechnology has become a crucial driving force for promoting the green transformation of industries such as production of energy, chemicals, materials, agriculture and manufacturing," Fano said.
"The waste oil and fats could be further reused to make profits. Today, more than 30 biodiesel plants around the world use enzymes to process a broad range of waste-based feedstock. We see a great potential for developing biotech solutions to fulfill the needs of more clients and partners in China," she added.