China, India can continue to learn from each other


Until the advent of steamships, the fastest way to get to India from China was to go to southern India first and then proceed northward. This was because India's long coastline is mostly in the south, and the southwest monsoon and northeast monsoon seasonal winds blow over different parts of South India, making travel possible throughout most of the year.
In addition, the Himalayas, which even today are a formidable barrier between northern India and China, were almost impenetrable during ancient times.
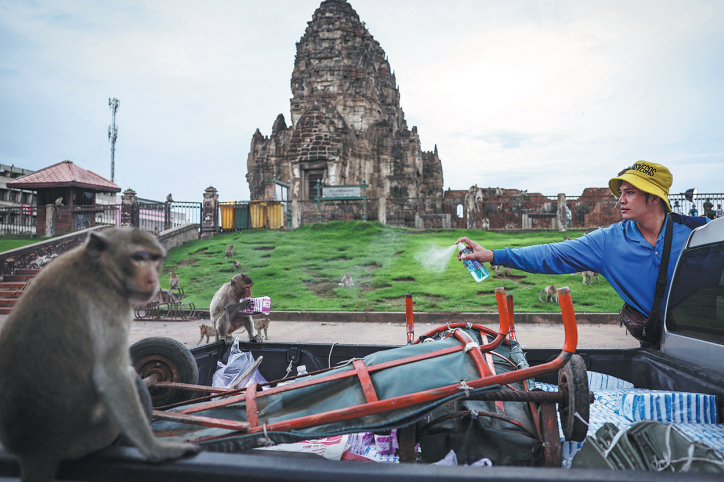
As President Xi Jinping prepares to visit the ancient city and modern metropolis of Chennai on southeastern India's Coromandel Coast on Oct 11, it may come as news to many in China that Buddhism came to China not from northern India, where Siddhartha Gautama, who was called Buddha, or "enlightened one", was born, but through southern India, because trade routes from India to China depended on "trade winds". Many people claim that not just Buddhism, but Chinese kung fu itself was brought to China by the southern Indian monk Bodhidharma, though hard evidence is lacking.
Legend and some historical sources claim Bodhidharma was the third son of a king who gave up royal life, like Buddha, to become a monk. Even before Bodhidharma, trade between India and China was flourishing and the word cheeni for sugar in some parts of India may indicate its Chinese origins. Similarly, cotton went from India to China and led to prosperity in central China.
The Chennai area is called Tamil Nadu (Land of Tamils), and the kings from this area in ancient times not only allowed trade but often financed and participated in it. So the wealth of southern India and the southern Indian kings depended to a large extent on trade, and this made the kings and society in southern India outward-looking and more open to new ideas and technology.
This was not the case in the landlocked northern Indian plains, where the kings depended on land taxes and were mostly suspicious of trade and the outside world.
Given this schism between North and South India, it is not surprising that the "knowledge" industries predominate in South India, whereas the "heavy" industries based on coal and iron ore predominate in the North. Chinese company Huawei has a large research lab in Bangalore, not far from Chennai, and many of China's IT companies have a presence in South India, while many of the Indian IT companies present in China in the area of Hangzhou, Zhejiang province, originated in southern Indian cities.
It is therefore appropriate that a Chinese president should be visiting Chennai for the first time in modern times.
As India seeks to emulate China, at least in the economic sphere, South India may have many things to learn from China and President Xi's visit.
Even as early as the Han Dynasty (206 BC-AD 220), Chinese chronicles mention Huang Zhi Guo, which most historians regard as the contemporary town of Kanchipuram near Chennai.
The visit of famous Chinese Buddhist monk Xuan Zang to India for 18 years (627-645) has been well documented. Xuan Zang definitely visited Kanchipuram. He says in his notes that "the land is fertile and crops flourish" and it "is a land of treasure teeming with flowers and fruits. The climate is warm. People are brave and staunch with moral integrity. They are deep in righteousness, well learned and noble-minded."
China and India have been trading and learning from each other for thousands of years, long before the European Renaissance. May that tradition continue as Xi visits Chennai.
The author is an entrepreneur focusing on Southeast Asia and the Indian subcontinent. The views do not necessarily reflect those of China Daily.