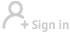Space lab edges closer to flaming finale

Tiangong I, China's first space laboratory, is expected to re-enter the atmosphere between March 31 and April 4, ending its nearly six and a half years in orbit with a light show, as most of it burns away in the sky and the rest falls into the ocean.
As of Sunday, the space station remained intact and in orbit more than 200 kilometers above the ground, according to the China Manned Space Agency. It will re-enter the atmosphere soon, and the agency said it will provide daily status updates on its website.
Launched on Sept 29, 2011, Tiangong I-also known as Heavenly Palace-is a key part of China's plan to develop its own manned space station similar to the International Space Station by the early 2020s.
The Chinese prototype station weights around 8.5 metric tons, and is 10.4 meters long and 3.4 meters wide, with 15 cubic meters of habitable internal volume, according to the space agency.
It consists of two primary components: an energy module, which contains the lab's solar power and propulsion systems; and an experimental module, in which astronauts conduct scientific work.
Tiangong I had completed six space rendezvous and docking missions with three visiting spacecraft. The first visit was by an unmanned spacecraft called Shenzhou VIII in November 2011, as part of China's first space docking mission.
The second and third missions were both manned: Shenzhou IX in June 2012 and Shenzhou X in June 2013. Both manned missions had three astronauts and lasted about two weeks, during which the astronauts tested the station's various systems and living conditions.
Tiangong I was designed to operate for just two years, but it officially completed its mission on March 16, 2016 and began its gradual decent.
"It has comprehensively fulfilled its historic mission," the agency said in an online statement at the time.
Meanwhile, Chinese scientists have been testing other space-related technologies on the falling station, including remote sensing, design, control and management for low orbit manned spacecraft. These tests yield valuable data that will help build China's future space station, the agency said.
The Aerospace Corporation, a nonprofit organization in the United States, estimated that the re-entry of Tiangong I would occur over Spain, France or Portugal, though an exact location is still hard to pinpoint.
Most of the station will burn away in the Earth's atmosphere, with the rest falling into the ocean. The chance of hitting someone is extremely unlikely, the agency said in an online statement in January.
However, a highly toxic and corrosive substance called hydrazine, which is often used in creating potent rocket fuel, can potentially survive re-entry.
"For your safety, do not touch any debris you may find on the ground or inhale vapors it may emit," the statement said.
- 'Ferryman of souls' escorts cremains of veterans from Taiwan to mainland home
- China announces month-long online shopping event for Spring Festival
- Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge reports record high passenger flows in 2024
- China launches action plan to tackle dementia amid aging population challenge
- Three found dead from overturned hoisting cage in Hohhot
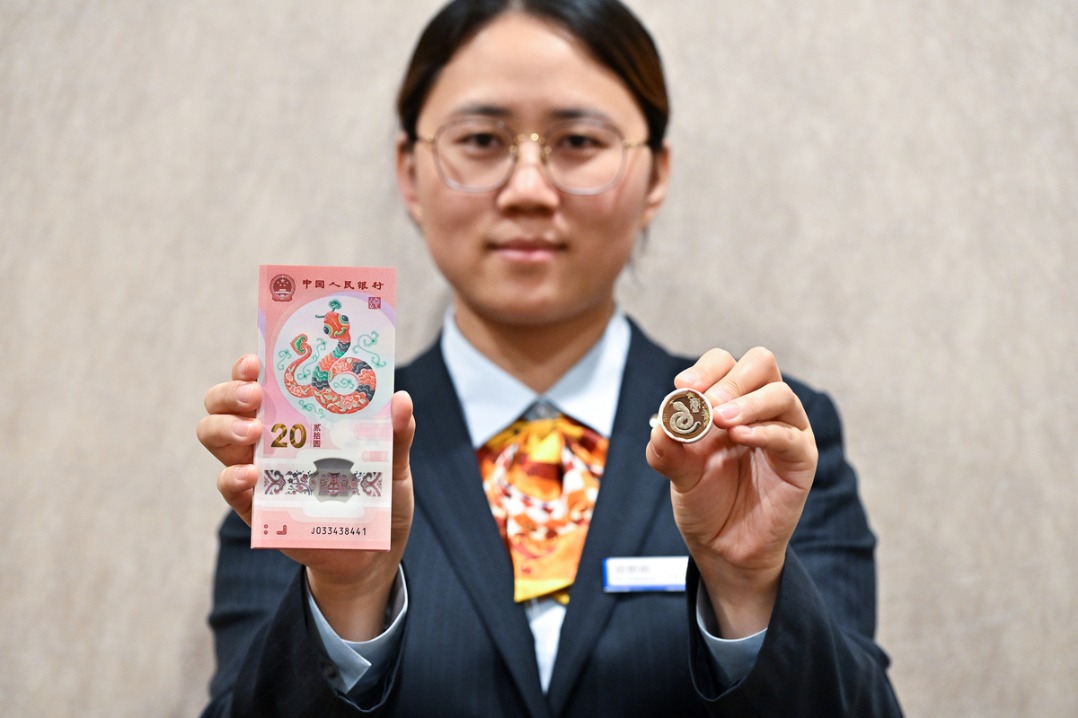
- Spring Festival coins, banknotes start to exchange